Ashish Tiwari's blog
The secret of mantras >> Managing is about how you manage your life well, it impacts your business and people.
Ultimately it is the people who manage business of your business, not you.
If your energy is in burning in your business, stop what you are doing, calm your mind, and relax. First take an eagle eye of view on your daily work affairs. Something a particular thing what you are doing in your business causes most of the energy burn. Find the misconception, remove the self bias & solve the issue pragmatically.
Find out what motivates you in your business life, and empower people involved in your business to help you with execution, bring focus on your business goals and hustle towards shaping your business and people growth.
The goal of any business is to increase customer benefits for customers, andgive higher returns to stakeholders. To increase customers benefits, the answers lies in competition benefits.
To increase business
economy, increase customer satisfaction & reduce the competition. You
have to manage internal as well as external cost’s well.
The overall approach has to be performance-&-evolution based business-management with an aim to win & satisfy more-customers, by your organizations internal stakeholders (directors, investors, financing, top management, workforce, reporting process, products, vendors, service, relationship) have to be aligned with your strategic mission. They should perform in perfect-harmony to overcome the external factors (competition/barriers, market, demand, and future).
What you need to focus on to make venture profitable is > a) Offering Value | b) Unit Economy | c) Competitiveness
LIFE > ENERGY > MOTIVATION > INCREASED CUTOMER-BENEFITS > HIGHER CUSTOMER-SATIFACTION WITH LESSER COMPETITION = Approach to business management.
1. Inability to organize detail, thus admitting inability to
do the job effectively.
2. Unwillingness to do what they would ask another to do,
when occasion demands.
3. Expectation of pay for what they know instead of what they do.
4. Fear of competition from others, trying to hold people below you rather than build them up.
5. Lack of creative thinking in setting goals and creating
plans.
6. The "I" syndrome – claiming all the honors for
the team achievements.
7. Over-indulgence, destroying endurance and vitality.
8. Disloyalty to colleagues, resulting in loss of respect.
9. Emphasis on the 'authority of leadership', leading by
instilling fear instead of encouraging.
10. Emphasis of title instead of knowledge and expertise.
11. Lack of understanding of the destructive effects of a
negative environment.
12. Lack of common sense, being heavenly minded and ultra positive, but no earthly good.
1. Fuzzy Vision - Corporate vision and mission don't inspire people; lack of strategic alignment; people don't know where the organization is going and what it is trying to achieve in the future.
2. Lack of Leadership Skills - Fear of change > Leaders lack entrepreneurial spirit; leadership style on the part of management is either too directive or too hands-off; managers do not lead and don't manage change, they just administrate and micromanage; weak leadership development program.
3. Discouraging Culture - corporate culture does not > inspire people; no shared values; employees are not energized; lack of trust; blame culture; focus on problems, not opportunities; people don't have fun at work; diversity is not celebrated; failures are not tolerated; people lose confidence in their leaders and systems.
4. High Bureaucracy - Bureaucratic organizational structures with too many layers; high boundaries between management layers; slow decision making; too close monitoring of things and subordinates; too many tools and documents discouraging creative thinking; bureaucracy is tolerated.
5. Lack of Initiative - Employees are not empowered; poor motivation and encouragement; people do not feel their contributions make a difference; management fails to engage the organization effectively; people work defensively and not creatively, they do their job, and nothing more.
6. Poor Vertical Communication - People have no clue of the big picture and do not feel that their contributions are important; too much uncertainty; people don't know what top-managers are thinking and planning.
7. Poor Cross-functional Collaboration - Functional mindset; lack of cross-functional goals and cross-functional collaboration spirit; functional, no enterprise-wide business process management; no cross-functional management committees; lack of or powerless cross-functional teams.
8. Poor Teamwork - No organizational commitment to team culture; lack of shared and worthwhile goals; weak team leaders; team members who don't want to play as part of a team are tolerated; teams are too large; lack of shared rewards.
9. Poor Idea and Knowledge Management - Cross-pollination of ideas is not facilitated; no creativity, idea and knowledge management strategies and systems; "know-it-all" attitude; "not invented here" syndrome.
This toolkit will help you just not build competitive strategy but also help you focu on your stage of business and what key activity and resources needs to be assigned for continuity and growth of your business. Refer the table to create your own competitive strategy:
.jpg)
Average ones compete with others. Great ones compete with themselves.
If you want to make a difference, innovate and create much higher value, question everything, ask a lot of self-searching questions.
How to identify your personal aims - Answer the following questions as best you can and you will get the answers yourself:
1. What are my personal long-term and short-term goals?
2. What specific objectives must I meet in the next period of time?
3. How will I measure success towards my goals and what feedback do I have to check my results against my goals?
4. What new initiatives can I take to achieve beyond my current goals?
To Make a Contribution: Ask yourself these questions:
1. What do I want to contribute? What value do I want to create?
2. What am I told to contribute?
3. What should I contribute to achieve higher results?
4. Where and how can I achieve breakthrough results that make a big positive difference?
5. What qualities and abilities have I shown myself to possess? What abilities do I want to strengthen?
6.Am I always learning forward in order to get the fullest benefit from my own strengths, while helping others to do likewise?
The definition for SMART Goals is:
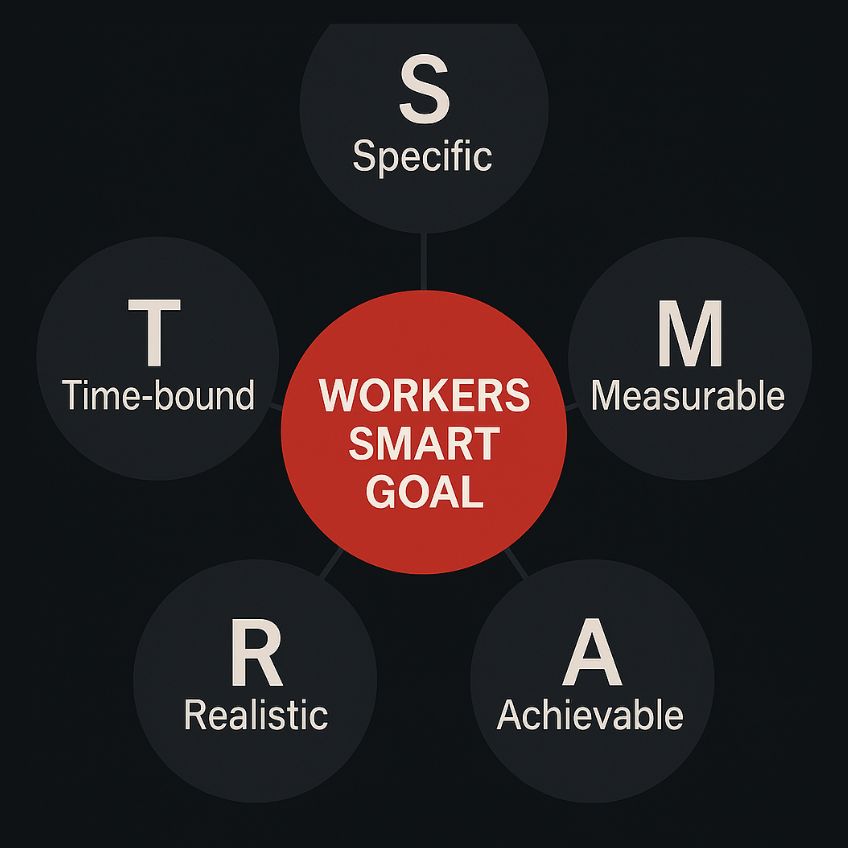
Specific – Clear and well-defined.
Measurable – Quantifiable to track progress.
Achievable – It is within inidviduals capability limits, and attainable.
Realistic – Practical given current resources.
Time-bound – Has a defined deadline.
But above is for workforce management, applying it as a frame on business is redundant and not wanted.
The definition of SMART Goals for Entrepreneurs is:
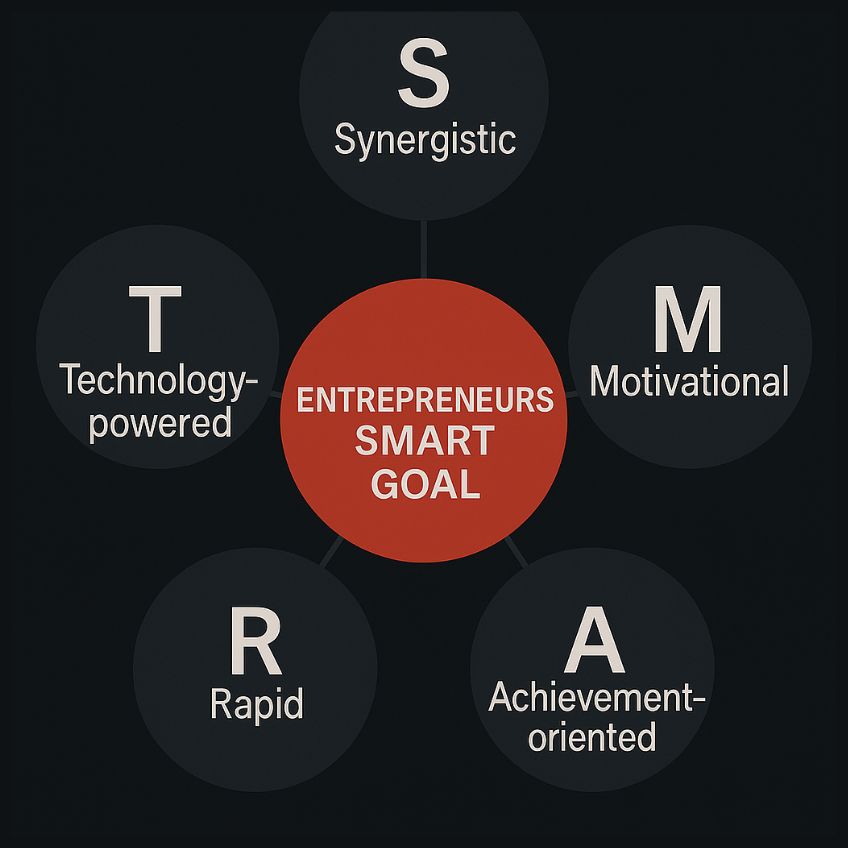
Synergistic – Aligns with departments, and broader ecosystems & partners.
Motivational – Inspires action and commitment.
Achievement-oriented – Focused on meaningful outcomes.
Rapid – Prioritizes speed and momentum.
Technology-powered – Leveraged through tools and innovation.
It is the art of leadership, how an entrepreneur applies own smart goals, with workers smart goal. That brings results!
Below are 5 main criterias to focus for having a Sustainable Competitive Advantage:
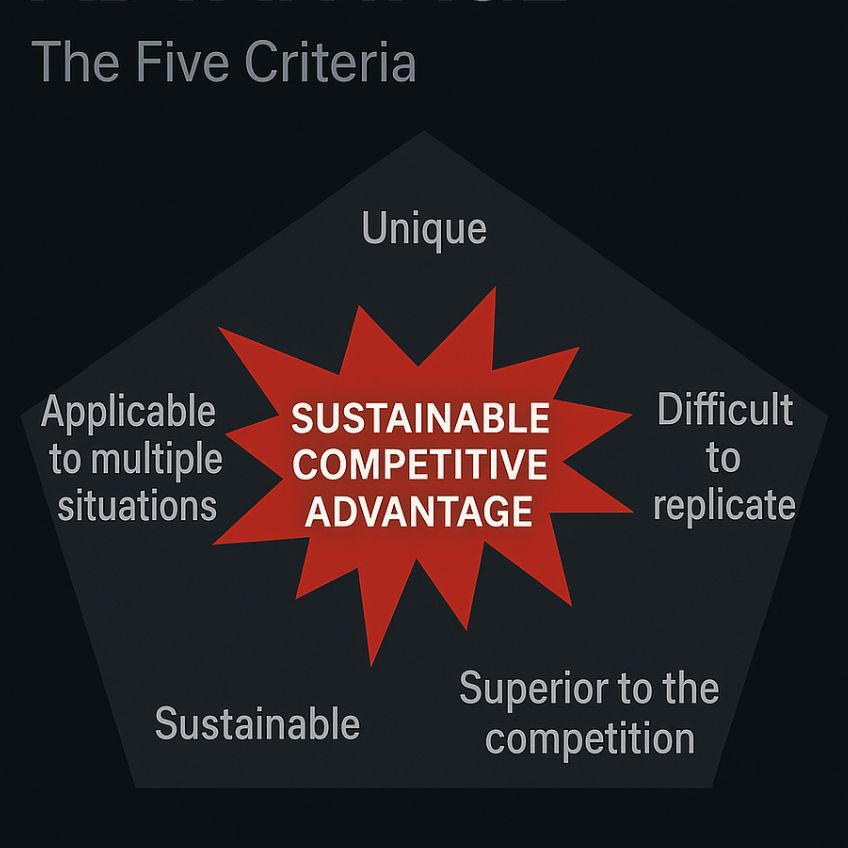
Sustainable competitive advantage is the prolonged benefit
of implementing some unique value-creating strategy based on unique combination
of a) internal organizational resources and b) capabilities that cannot be replicated
by competitors.
Competitive
Strategies
Case study 1 - Warren
Buffet's Investment Criteria - Warren Buffet was once asked what is the most
important thing he looks for when evaluating a company to invest in. Without
hesitation, he replied, "Sustainable competitive advantage."
Case study 2 - Amazon.com - New business model developed by
Amazon.com creates value for customers by offering a synergistic combination of
the following benefits:
> Shopping convenience
> Ease of purchase
> Speed
> Decision-enabling information
> A wide selection
> Discounted pricing
> Reliability of order fulfillment
No single aspect of Amazon.com's business model is
sufficient to create a sustainable competitive advantage. It is the synergistic
combination of all of these information services and logistical processes that
creates value for customers and comprise Amazon.com's competitive advantage.
Case study 3 - Toyota - Toyota’s global competitive
advantage is based on a corporate philosophy known as the Toyota Production
System. The system depends in part on a human resources management policy that
stimulates employee creativity and loyalty but also on a highly efficient
network of suppliers and components manufacturers.
Workforce advantage of Toyota - Create a workforce that
would provide a competitive advantage
"An intelligent and integrated human resources strategy
is the only sustainable competitive advantage... Every other corporate asset
can be bought or replicated virtually overnight, but competitors seeking to
duplicate a well-trained, motivated, and committed workforce will need at least
a decade to catch up. Exceptional cultures just can't be created
with the wave of wand – or a major infusion of capital," says Mark
Stevens, the author of Extreme Management.
How to finalize its execution process:-
Build on Your Core Competencies - The core competencies are the things your company can do better than your competitors. If a core competency yields a long term advantage to the company, it is said to be a sustainable competitive advantage. As a leader, you must focus your firms resources on what it does best and what creates competitive advantage. Some technical and business competencies can be in short supply however. You can address these missing competencies by using three approaches: internal development, acquisition of an outside firm, and partnering.
Focus on Your Competitive Advantage - Focus on your core competencies and outsource the rest. Make sure that you don't outsource your competitive advantage. You will never lead in innovation or be faster to market than your competition if you depend on other for your core technology. Owning your competitive advantage will allow you to build it continuously, be more flexible, and eliminate speed breakers.
Barriers to Entry - Barriers to entry are circumstances particular to a given industry that create disadvantages for new competitors attempting to enter your market.
The Role of Intellectual Property Rights and Strategy - In most industries, intellectual property rights (IPR), especially patents and their exploitation, hold key significance in the development and commercialization of new products. Businesses should have an intellectual property strategy as part of their corporate planning and strategy.
Winning organizations always shows energy, movement, change and development. It consists of Leadership, culture, empowered employees who are performing with their full capabilites.
Below is a readymade checklist to evaluate your organization to discover opportunities for improvement:
Leadership is GOOD when:
1. Vision inspires and energizes all employees
2. Leaders are energized, communicates strategic direction, and lead by example
3. Inspire and energize people, provide coaching
4. Creates positive change and see change as an opportunity
Culture is GOOD when:
1. Shared values link the organization together; all employees live the values
2. Culture inspires people and nurtures an attitude of relentless growth
3. Team culture reigns, teams are infused with purpose, personality, and passion
4. Customer-focused quality culture and continuous improvement culture established
Empowered Employees are GOOD when:
1. People are sharply aligned with vision and strategies
2. Individuals and teams are empowered and have a decision-making authority
3. People hate bureaucracy relentlessly at all organizational levels
4. Innovators have freedom to experiment, fail, and begin again more intelligently
Performance Management is GOOD when:
1. Motivation systems encourage extraordinary performance from all employees
2. Suggestion systems involve all employees in continuous efficiency improvement
3. Coaching environment helps people unlock their true potential
4. Effective performance measurement system is established
Capabilities are GOOD when:
1. Effective creativity, idea and knowledge management systems are established
2. Teamwork is made a religion, cross-functional innovation teams are empowered
3. Cross-functional synergies are exploited, diversity is leveraged
4. Leadership development programs help grow leaders at all organizational levels
Every successful entrepreneur, every successful businessperson has been someone who's been able to creating an innovative customer value by identifying a problem and coming up with a solution to it before somebody else did.
Case in Point Jim Clark - Jim Clark is a serial entrepreneur who became a billionaire in the 'Internet age'. He was involved in starting Netscape, Silicon Graphics and many other start-up ventures.
When asked "What Traits Should Every Good Entrepreneur Possess?", Jim answered, "Discontent and anxiety. Most entrepreneurs are not content with the way things are. But if they're smart, they're extremely anxious too. Most ideas are going to happen whether you do them or someone else does. It's the person who feels most anxious about it and builds the prototype who is likely to win. The best entrepreneurs tend to move quickly and efficiently. They don't waste a lot of time making decisions!
2. Active learning and learning strategies
3. Complex problem solving
4. Critical thinking and analysis
5. Creativity, originality and initiative
6. Leadership and social influence
7. Technology use, monitoring and control
8. Technology design and programming
9. Resilience, stress tolerance and flexibility
10. Reasoning, problem solving and ideation